Aplicação da soldagem a laser em linhas de montagem de baterias para armazenamento de energia.
Desde a fabricação de células de baterias para armazenamento de energia até a montagem de conjuntos de baterias, a soldagem é um processo de fabricação crucial. A condutividade, a resistência, a estanqueidade, a fadiga do metal e a resistência à corrosão das baterias de lítio são padrões típicos de avaliação da qualidade da soldagem de baterias. A seleção de métodos e processos de soldagem afeta diretamente o custo, a qualidade, a segurança e a consistência da bateria.
Dentre os diversos métodos de soldagem, a soldagem a laser se destaca pelas seguintes vantagens: Primeiro, a soldagem a laser possui alta densidade de energia, pequena deformação e uma pequena zona afetada pelo calor, o que pode melhorar efetivamente a precisão das peças, resultando em soldas lisas, isentas de impurezas, uniformes e densas, sem a necessidade de retificação adicional.
Em segundo lugar, a soldagem a laser pode ser controlada com precisão, com um ponto focalizado pequeno e posicionamento de alta precisão. Combinada com braços robóticos, é fácil de automatizar, melhorando a eficiência da soldagem, reduzindo o tempo de trabalho e diminuindo os custos. Além disso, ao soldar chapas finas ou fios de diâmetro reduzido, o laser não está sujeito ao problema de refusão tão facilmente quanto na soldagem a arco.
Os principais métodos de soldagem para baterias de armazenamento de energia incluem soldagem por onda, soldagem ultrassônica, soldagem a laser e soldagem a laser de metais diferentes, sendo a soldagem a laser atualmente o método mais comum.
Métodos de soldagem de baterias de armazenamento de energia:
① Soldagem por onda
Essencialmente, uma combinação de soldagem ultrassônica e soldagem a laser;
② Soldagem ultrassônica
Este método é simples de usar, mas requer mais espaço, resultando em menor eficiência na montagem dos módulos;
③ Soldagem a laser
Atualmente, é o método mais utilizado, mas com ligeiras diferenças estruturais;
④ Soldagem a laser de metais diferentes
Este método de soldagem também apresenta alta eficiência de montagem e velocidade de produção rápida.
O que é soldagem a laser?
A soldagem a laser utiliza um sistema óptico para focalizar um feixe de laser de alta densidade de energia como fonte de calor em uma área muito pequena, criando uma zona de calor altamente concentrada no local da solda em um curto período de tempo. Isso funde os materiais a serem soldados, formando um ponto de solda ou cordão de solda resistente.
A soldagem a laser é um novo método de soldagem que se encontra em rápida fase de desenvolvimento. Ela oferece diversas vantagens: menor zona afetada pelo calor, pontos de solda menores, maior precisão dimensional e soldagem sem contato, que não requer força externa, resultando em mínima deformação do produto, alta qualidade da solda, alta eficiência e facilidade de automação.

As baterias normalmente incorporam diversos materiais, como aço, alumínio, cobre e níquel. Esses metais podem ser usados para formar eletrodos, fios ou invólucros. Portanto, a soldagem entre um ou mais materiais impõe altas exigências ao processo de soldagem.
A vantagem da soldagem a laser reside na sua capacidade de soldar uma ampla gama de materiais, permitindo a soldagem entre materiais diferentes.
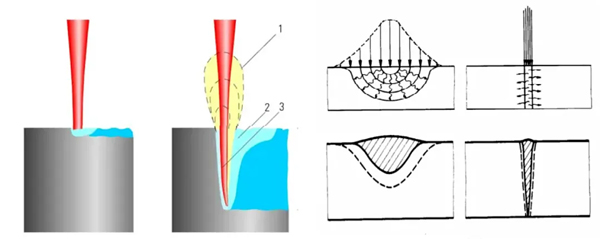
Tipos de soldagem a laser
A soldagem a laser inclui a soldagem por condução térmica a laser e a soldagem por penetração profunda a laser. A principal diferença entre a soldagem por condução térmica e a soldagem por penetração profunda reside na densidade de potência aplicada à superfície do metal por unidade de tempo; diferentes metais possuem diferentes valores críticos.
Três lasers comumente usados para soldagem a laser de baterias de armazenamento de energia
As baterias de armazenamento de energia são um sistema integrado composto por dispositivos de armazenamento de energia (desde componentes individuais → módulos de baterias → gabinetes de baterias → unidades de armazenamento de energia → equipamentos de armazenamento de energia), PCS (Sistema de Controle de Energia) e componentes de filtragem.
Na área de soldagem a laser para baterias de armazenamento de energia, os lasers mais comumente usados são os lasers pulsados, os lasers contínuos e os lasers quase contínuos.
-
Lasers pulsados
Lasers YAG, lasers MOPA;
-
lasers contínuos
Lasers semicondutores contínuos, lasers de fibra contínuos;
-
Lasers quase contínuos
Série de lasers QCW.
Esses lasers podem ser compreendidos da seguinte forma: martelar uma tachinha em um único golpe de cada vez é um processo pulsado; pressionar a tachinha diretamente com a mão é um processo contínuo; perfurar continuamente por 10 segundos, descansar por um segundo, perfurar continuamente por mais 10 segundos e descansar por um segundo é um processo quase contínuo.
Lasers pulsados
Referem-se a lasers com uma largura de pulso única inferior a 0,25 segundos, operando apenas uma vez em intervalos regulares. Possuem alta potência de saída e são adequados para marcação, corte e medição de distância a laser.
Os lasers pulsados comuns incluem lasers de estado sólido, como os lasers de granada de ítrio-alumínio (YAG), lasers de rubi e lasers de neodímio em vidro, bem como lasers moleculares de nitrogênio e lasers de excímero. Os lasers pulsados são baseados no princípio do laser YAG, com alta energia de pulso único e alto consumo de energia, exigindo a substituição regular de consumíveis, como lâmpadas de xenônio, e necessitando de um sistema de resfriamento rápido.
Esses lasers são bastante consolidados, com custos unitários relativamente baixos, e atualmente são os mais utilizados para soldagem de metais. No entanto, devido às limitações tecnológicas baseadas no princípio do laser YAG, a indústria como um todo não consegue atingir uma potência de laser muito alta; a eficiência de conversão eletro-óptica não é elevada (em torno de 13%).
Lasers de onda contínua
São lasers que emitem luz continuamente, o que significa que possuem um estado operacional estável, ou seja, um estado estacionário. Em um laser de onda contínua, o número de partículas em cada nível de energia e o campo de radiação dentro da cavidade têm uma distribuição estável.
A característica operacional dos lasers de onda contínua é que a excitação do meio de trabalho e a correspondente emissão de laser podem continuar continuamente por um período de tempo relativamente longo. Lasers de estado sólido excitados por fontes de luz contínua, assim como lasers a gás e lasers semicondutores que operam por excitação elétrica contínua, pertencem a esta categoria.
Como o sobreaquecimento é frequentemente inevitável durante o funcionamento contínuo, a maioria requer medidas de arrefecimento adequadas.
Os lasers de onda contínua são baseados no princípio dos lasers de fibra YLP. Como podem emitir luz continuamente com potência constante (quando os pontos de emissão do laser são suficientemente rápidos e numerosos, eles são conectados em linha), a energia do laser de saída é constante, a estabilidade do laser é muito boa, o padrão do feixe é excelente e a eficiência de conversão eletro-óptica é muito alta (em torno de 30%).
ACEY tipo pórtico
máquina de soldagem a laser galvanométrica contínua
Utiliza um laser de fibra de última geração como fonte de energia. Combinado com a máquina-ferramenta de pórtico desenvolvida, projetada e fabricada pela nossa empresa, apresenta excelente rigidez e estabilidade. Opera com transmissão por trilho guia de precisão e está equipado com um servomotor de alta resposta, o que garante alta precisão e velocidade. É adequado para soldagem de cobre, alumínio, ferro, níquel ou suas ligas, sendo especialmente indicado para soldagem de barramentos de alumínio ou conexões de níquel em baterias.

Lasers de onda quase contínua (QCW)
Os lasers QCW, também chamados de lasers de pulso longo, produzem pulsos da ordem de milissegundos com um ciclo de trabalho de 10%. Isso permite que a luz pulsada tenha uma potência de pico mais de dez vezes maior que a luz contínua, o que é muito vantajoso para aplicações como perfuração. A frequência de repetição pode ser modulada até 500 Hz, dependendo da largura do pulso. Os lasers QCW podem operar simultaneamente nos modos contínuo e de pulso de alta potência de pico. Ao contrário dos lasers de onda contínua (CW) tradicionais, os lasers de onda quase contínua (QCW) sempre mantêm a mesma potência de pico e média nos modos CW e CW/modulação. Em contraste, a potência de pico de um laser QCW no modo pulsado é 10 vezes maior que sua potência média.
Portanto, isso permite a geração de pulsos de alta energia na faixa de microssegundos e milissegundos, com frequências de repetição que variam de dezenas de hertz a quilohertz, atingindo potência média e de pico de quilowatts.
Vantagens dos equipamentos de soldagem a laser em baterias de armazenamento de energia:
1. O processo de soldagem é sem contato, minimizando a tensão interna nas nervuras de solda.
2. O processo de soldagem não produz qualquer transbordamento ou liberação de substâncias, evitando a poluição secundária.
3. A solda apresenta alta resistência e estanqueidade, atendendo aos requisitos funcionais.
4. A soldagem a laser pode soldar diferentes materiais, incluindo materiais de membrana e materiais distintos.
5. A soldagem a laser é facilmente integrada a sistemas automatizados e pode ser implementada de forma síncrona de acordo com as necessidades de capacidade de produção, resultando em alta eficiência e baixo estresse interno.
6. A soldagem a laser envolve estruturas simples e práticas, reduzindo a complexidade das estruturas dos moldes.
7. O processo de soldagem pode ser monitorado digitalmente e de forma inteligente, atendendo à necessidade de visualização de dados.
8. Este tipo de processo de soldagem pode ser integrado de forma eficaz com linhas de produção automatizadas, atendendo às necessidades da produção em massa e alcançando alta eficiência produtiva com baixo consumo.
Acey Nova Energia
é especializada no fornecimento de equipamentos de produção completos e soluções integradas para
linha de montagem de baterias de íon-lítio
—da célula ao pacote—feito sob medida para iniciantes no campo de armazenamento de energia em baterias de lítio. Seja no planejamento da linha de produção, na integração de equipamentos ou em etapas-chave como empilhamento de módulos, soldagem a laser, integração do BMS e testes finais do pacote, oferecemos suporte técnico confiável e sistemas de produção eficientes e estáveis. Recebemos com satisfação clientes de todo o mundo e esperamos ser seu parceiro profissional e confiável para construirmos juntos um futuro melhor.


